Systematics
1. Systematics is the study of (internal systems, heredity, genes, methods of sorting, organs) ________________________________.
2. Taxonomy is the study of __________________________________________.
3. Phylogeny is the study of _________________________________________.
4. Name two ways in which organisms can be sorted _____________________________ and _________________________________.
5. What is a genome? ____________________________________________________________________________________________.
6. How does an Electrophoresis sort fragments of DNA _____________________________________________________________.
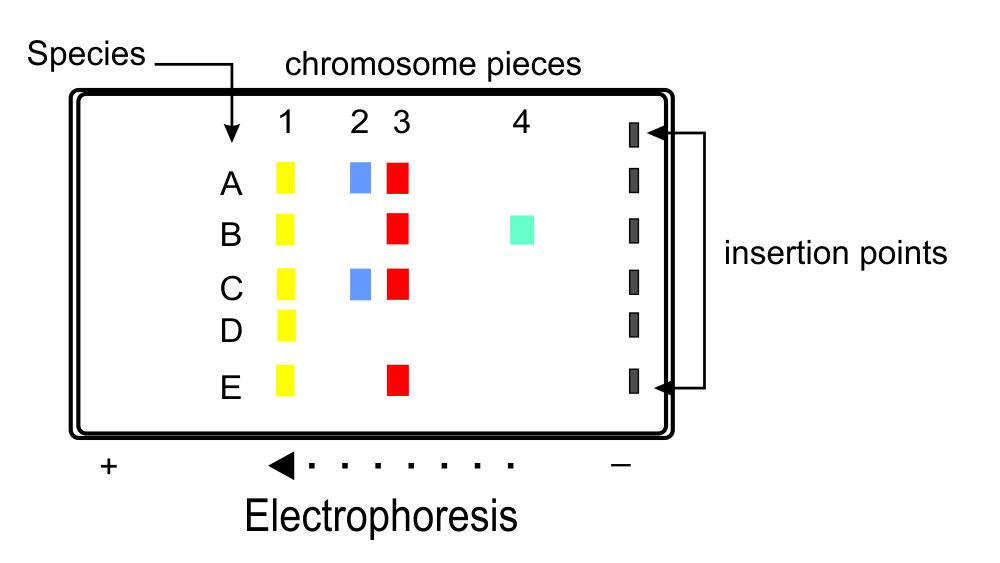
7. The groups sorted above show five rows of colors, labeled from the top to the bottom as A, B, C, D and E. Which one of the rows would represent the beginning of the group, (the one that all others would spring from)?
_____________
8. Which row (letter A, B, C, D or E) would represent most recent evolved organism? ______________________________.
9. Which two rows would show the greatest degree of close relationship? ________________________ and _________________________.
10. The row bands shown are different colors and different widths, what do those bands actually represent? _______________________________________.
11. What makes the single spots of color move apart into a separate arrays (rows) of colors? _____________________________________________________.
12. Which of the colors represents the smallest molecule (column number)? __________________________________.

The horse on the left (A) and the chimpanzee on the right (B).
13. What are the two most important senses for the horse (as determined by the skull)? _________________________________ and ___________________________.
14. The chimpanzee and the horse have their eyes pointing differently. From these animal's eye placement, which animal would have better depth perception? ___________________________ Why? ______________________________________
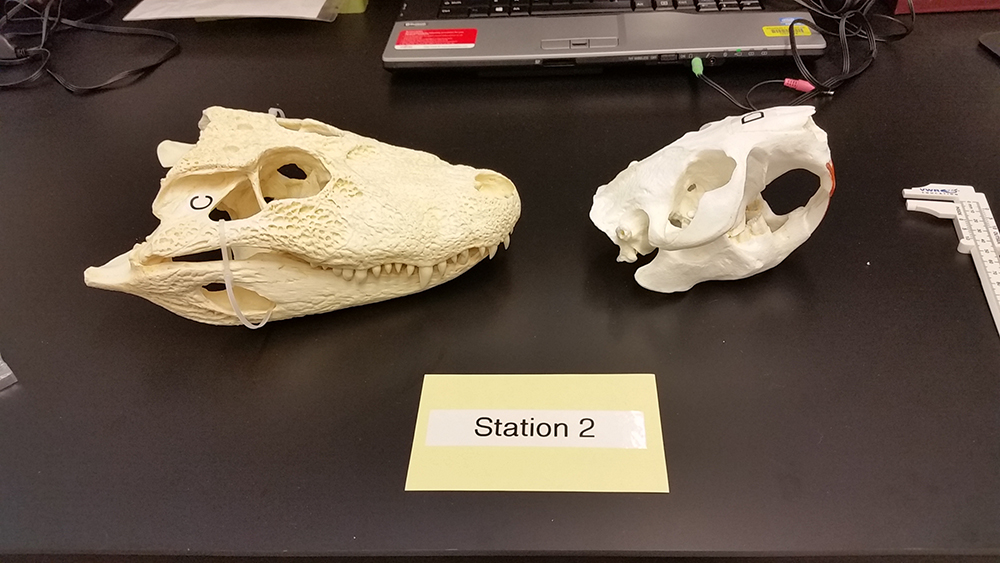

The alligator on the left (C) and the beaver on the right (D).
15. Which animal, based on the skull (jaw) would have the greater biting force? ___________________________________
16. The alligator skull has how many kinds of teeth? _________________________
17. How does the alligator handle its prey? __________________________________________________________________
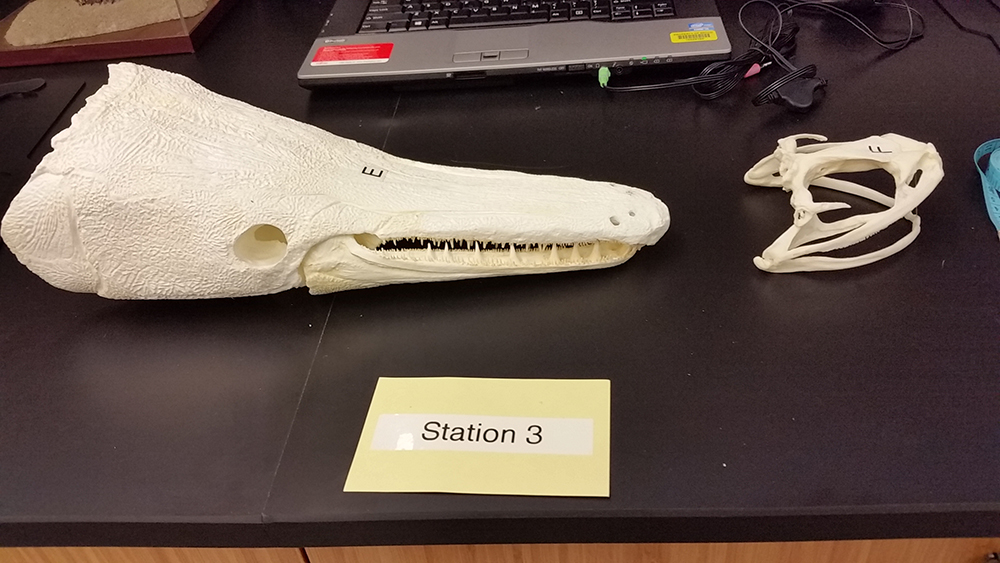

Alligator Gar (fish) on the left (E) and a bullfrog on the right (F).
18. The alligator gar (fish) and the bullfrog (amphibian) have one thing in common, what is it? ____________________________________________________________
19. The eyes and nostrils of the bullfrog are on top of the head, Why? _________________________________________________________________

An Owl on the left (G) and a turkey on the right (H).
20. These birds cannot chew their food, how are the able to consume their prey? ________________________________________________________
21. Since the Owls hunt at night, what is the single best adaptation they have (as seen by the skull)? ___________________________________________________________
22. Is the turkey a night-time predator? _________________________ What do you base you decision on? _______________________________________
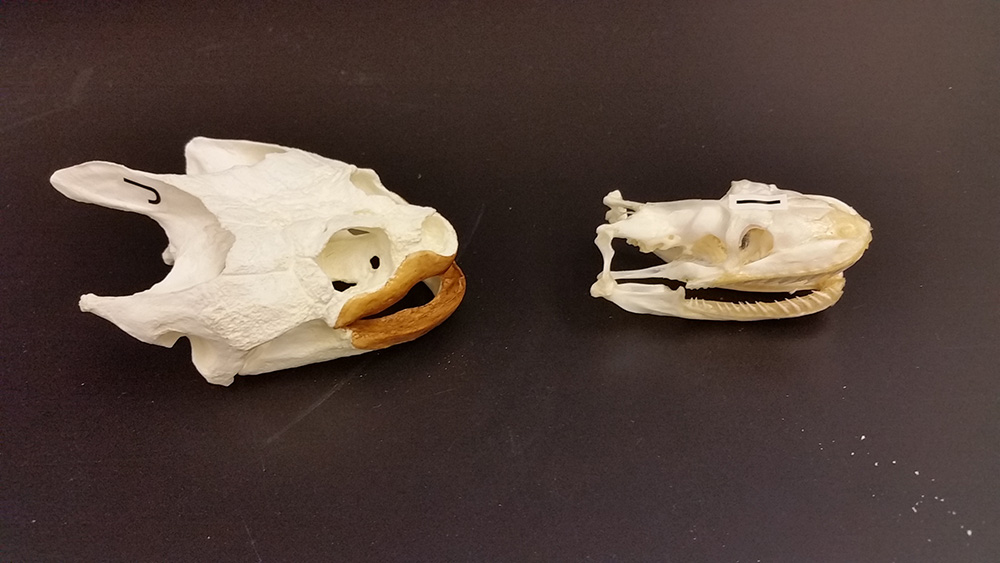

The snapping turtle on the left (J) and the snake skull on the right (I).
23. How does the snapping turtle (no teeth) consume it prey? ____________________________________________________
24. The snake has only pointed teeth, how does the snake consume its prey? _______________________________________
25. The snake can disarticulated its jaw (move it away from the hinge), how does this action help it to consume its prey? ________________________________

A coyote skull on the left (K) and a cat skull on the right (L).
26. What attributes do these two skulls share in common? __________________________________________________________
27. Are these two animals predators or prey? _________________________________________________________________________
28. What are the large dagger-like teeth for? ____________________________________________________________________________
29. A series of contrasting statements that enable the reader to distinguish the name of an organism is called a _________________________ key.






